Vulnerability management is the ongoing, regular process of identifying, assessing, reporting on, managing and remediating cyber vulnerabilities across endpoints, workloads, and systems. Typically, a security team will leverage a vulnerability management tool to detect vulnerabilities and utilize different processes to patch or remediate them.
A strong vulnerability management program uses threat intelligence and knowledge of IT and business operations to prioritize risks and address vulnerabilities as quickly as possible.
A vulnerability, as defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO 27002), is “a weakness of an asset or group of assets that can be exploited by one or more threats.”
A threat is something that can exploit a vulnerability.
A risk is what happens when a threat exploits a vulnerability. It’s the damage that could be caused by the open vulnerability being exploited by a threat.
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate the severity and characteristics of software vulnerabilities. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. The CVSS v3.0 scores and associated ratings are as follows:
| CVSS Score | Severity Rating |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | None |
| 0.1-3.9 | Low |
| 4.0-6.9 | Medium |
| 7.0-8.9 | High |
| 9.0-10.0 | Critical |
NVD also provides a regularly updated library of common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs), providing the rankings and other associated information (such as vendor, product name, version, etc.). The list of CVEs originate from the MITRE Corporation. MITRE is a not-for-profit organization that began documenting CVEs in 1999. It provides basic information about each vulnerability and is automatically synced with NVD.
Vulnerability management is different from vulnerability assessment. Vulnerability management is an ongoing process, while a vulnerability assessment is a one-time evaluation of a host or network. Vulnerability assessment is part of the vulnerability management process, but not vice versa.
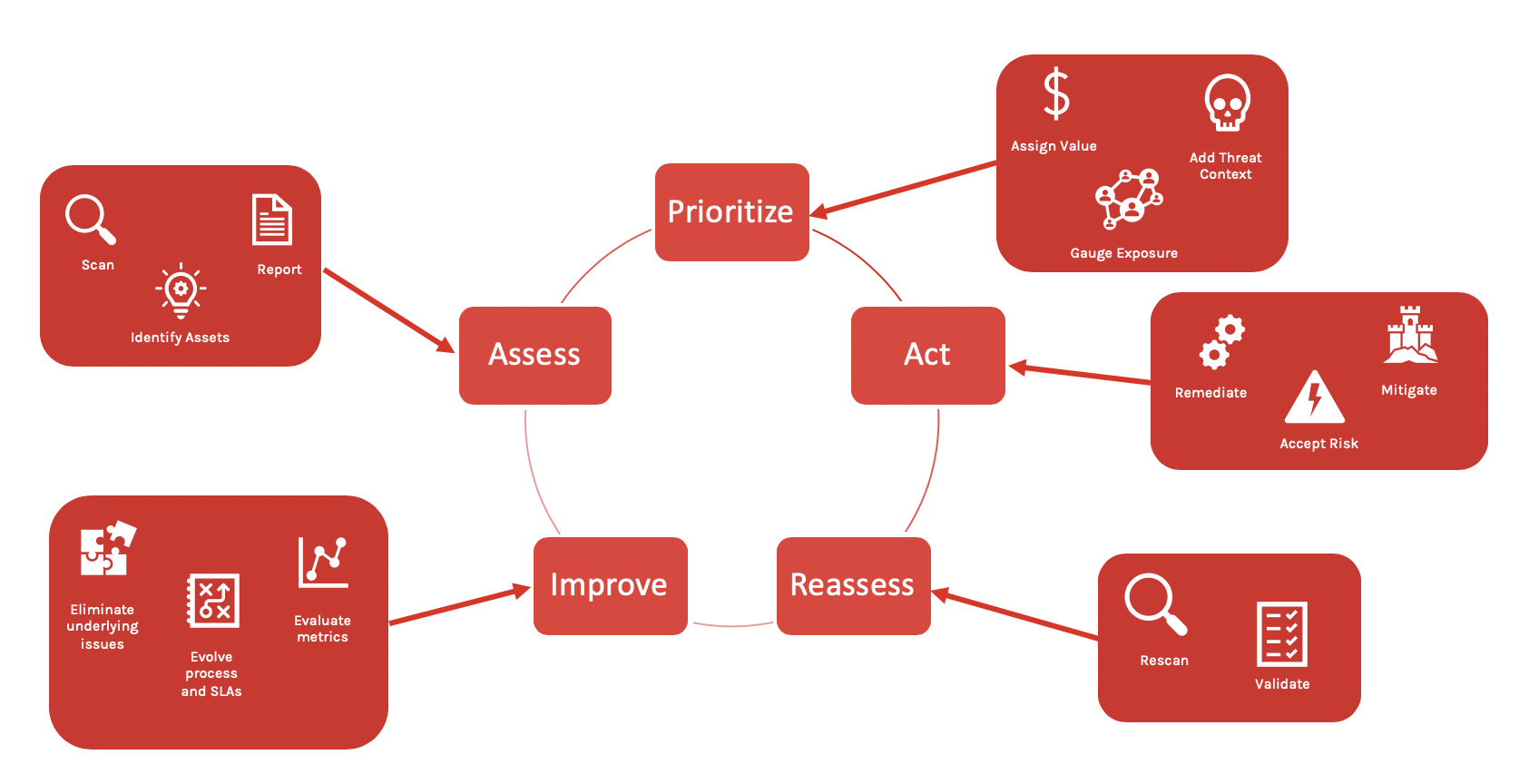
There are several stages in the vulnerability management process that vulnerability management programs should adhere to. While there are different ways to define each stage in the cycle, the process is still generally the same, even if the terminology varies.
Gartner’s Vulnerability Management Guidance Framework lays out five “pre-work” steps before the process begins:
This pre-work stage assesses and measures current resources, processes and tools in order to identify gaps.
During the pre-work phase, a security professional should ask questions that can help determine the scope of your program, including:
With this information, you can begin the implementing the vulnerability management process.
There are five main stages in the vulnerability management cycle include:

Follow along as we break down each step of the vulnerability management process and what it means for your organization’s program.Vulnerability Management Lifecycle Deep Dive
Managing exposure to known vulnerabilities is the primary responsibility of a vulnerability manager. Although vulnerability management involves more than simply running a scanning tool, a high-quality vulnerability tool or toolset can dramatically improve the implementation and ongoing success of a vulnerability management program.
The market is filled with options and solutions, each claiming leading qualities. When evaluating a vulnerability management solution, keep these things in mind:
Timeliness is important. If a vulnerability management tool fails to detect vulnerabilities in a timely manner, then the tool isn’t very useful and doesn’t contribute to overall protection. This is where network-based scanners often fail. It can take a long time to complete a scan and consume a large portion of your organization’s valuable bandwidth only to produce immediately outdated information. It’s better to choose a solution that relies on a lightweight agent rather than on a network.
Performance impact on an endpoint is key. Increasingly, vulnerability scanning vendors claim to offer agent-based solutions. Unfortunately, most of these agents are so bulky that they dramatically impact an endpoint’s performance. Therefore, when searching for an agent-based tool, look for one with a lightweight agent — one that consumes very little space on an endpoint to minimize any effect on productivity.
Real-time, comprehensive visibility is critical. You should be able to see what’s vulnerable in an instant. Legacy vulnerability tools can hinder visibility — network scans take a long time and provide outdated results, bloated agents slow business productivity, and bulky reports do little to help address vulnerabilities in a timely manner. Scan-less technology such as Falcon Spotlight allows your team to see and interact with data in real time. A single interactive dashboard with search and filter features allow you to act immediately to close potentially dangerous gaps in your organization’s security. Because it is a scan-less solution, it is always running, constantly looking for weaknesses and identifying vulnerabilities.
Less is more. Organizations no longer need a complicated set of security tools and solutions that require personnel with specialized skills. Instead, many now rely on an integrated platform that includes vulnerability management tools along with other security tools for cyber hygiene, endpoint detection and response, device control and more — ultimately protecting your organization from attack due to unprotected systems.

Download the Falcon Spotlight Data Sheet to learn CrowdStrike’s approach to vulnerability management.